Covid Monitoring
Rapid COVID-19 testing for JPL environmental surfaces using the CDC/NIH assay
BPPG MARS 2020
The JPL PP team members and NASA’s Mars exploration program at Kennedy Space Center
μTITAN TESTING
The “Omics In Space” team develops a novel DNA extraction device for ISS
LETTER FROM MANAGER
 Alvin L. Smith, Ph.D., PMP
Alvin L. Smith, Ph.D., PMP
Manager of Planetary Protection Center of Excellence
It is again my pleasure to connect with the many stakeholders and supporters planetary protection at JPL and the Planetary Protection Center of Excellence (PP CoE). I truly hope that you all enjoyed the inaugural issue of “The Microbe.” We are happy to have this publication and share the exciting work and accomplishments of the Biotechnology and Planetary protection Group (BPPG) and PP CoE, to include our newly designed logo. Our new logo represents our fundamental goal of supporting NASA's ability to preserve the scientific integrity of current and future solar system exploration for life detection, which represented by the planets and DNA helix.
The last several months have been very difficult for all of us. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, and its pervasive reach, have impacted every facet of American life. But, no matter the challenge, the BPPG and JPL as whole has worked hard to show the true resilience of our JPL family and our dedication to the success of NASA missions and commitment to scientific exploration.
As you will read in this issue, our PP engineers and scientists, led by Dr. Kasthuri Venkateswaran, were instrumental in keeping JPL moving forward during the pandemic by answering the Director’s call to provide COVID-19 environmental monitoring of our JPL cleanrooms and other public areas as we finalized Mars 2020 operations on Lab and at Kennedy Space Center. We also salute Dr. Moogega Cooper and her team on their stellar support and sacrifices made to ensure the on-time sampling and delivery of products necessary for an on time launch of the Mars 2020 rover. On February 18, 2021 we all celebrated our PP implementation success, with the rest of the nation, as we landed Perseverance and Ingenuity on Mars, after their long journey.
Last summer, like many other organizations, JPL had to adjust to the new normal of hosting hundreds of virtual internships rather than the familiar sight of almost 1000 students on Lab. Even during the pandemic and our ongoing support to M2020, the BPPG and the CoE were able to support 16 PP interns and faculty from across the nation with overwhelming majority from Historically Black Colleges and Universities, a first for the group. Many thanks are extended to Drs. Zach Dean, Parag Vaishampayan, and Chiranjit Mukherjee for their unwavering commitment to train the next generation PP engineers and scientists. Their stories are also highlighted in this issue and we look forward to similar success this year with the virtual bioinformatics “VOICES” program.

If nothing else, I hope this issue demonstrates that it takes all of us working together to persevere through tough these times while continuing to live up to the JPL motto to “Dare Mighty Things.” I hope you all will enjoy our second issue and continue to support the BPPG and the PP CoE.
Covid Monitoring
BPPG Expertise Ensures JPL Safety and Mission Success Amid COVID-19 Pandemic
On March 19, 2020, the Governor of California issued a statewide stay at home order for non-essential workers in order to fight SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19. At the time of the order, COVID-19 had already caused 23 deaths in California and over 10,000 deaths worldwide. The following day and after a discussion with NASA headquarters, JPL leadership implemented a no-access policy to nearly all JPL personnel in order to conform to the mandates. While affecting many research tasks, the JPL order did exempt mission-essential personnel for Mars 2020 and required staff, albeit limited, to protect current mission operations in addition to the safety and security of critical hardware and lab facilities. Any exceptions, regardless of duration, needed to be worked through JPL Line or Project Management in addition to being authorized by the Protective Services Division Manager.
As JPL was preparing for the Mars 2020 Perseverance Rover launch, and to mitigate the risk of any delay from COVID-19, the BPPG JPL Planetary Protection (PP) team proposed a plan to monitor JPL common areas, such as conference rooms and clean rooms, for SARS-CoV-2 surface contamination in addition to developing countermeasure strategies to mitigate the virus. JPL engineers, together with industry partnerships, combined their expertise and facilities to develop rapid virus detection systems to combat SARS-CoV-2 and curb potential COVID-19 exposure on Lab.
Meanwhile, JPL PP employed quantitative real-time polylymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and modified existing protocols, based on Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines, in order to develop a detection pipeline to spot SARS-CoV-2 on environmental surfaces. The CDC/NIH-based pipeline is capable of distinguishing the SARS-CoV-2 virus from other common, related viruses. Since the CDC/NIH qPCR primer sets can cover all known COVID-19 disease causing viral strains, they helped provide guidance to JPL leadership on the prevalence of the virus at JPL.
The PP COVID-19 monitoring pipeline included the following steps: 1) swab collection of JPL environmental surfaces, 2) preservation of samples with a DNA/RNA shield, 3) automated RNA extraction, 4) viral detection and quantification and 5) archiving of extracted RNA for future monitoring. If a sample tests positive for COVID-19, three additional steps are executed: a) sequence the extracted RNA with nanopore sequencing, b) analyze the sequences for genetic information and viral species identification, and c) record/report the results. Additionally, in-depth metadata from sample collection to results reporting and follow up tests was captured with a JPL-designed app, specifically created for the COVID-19 task force.
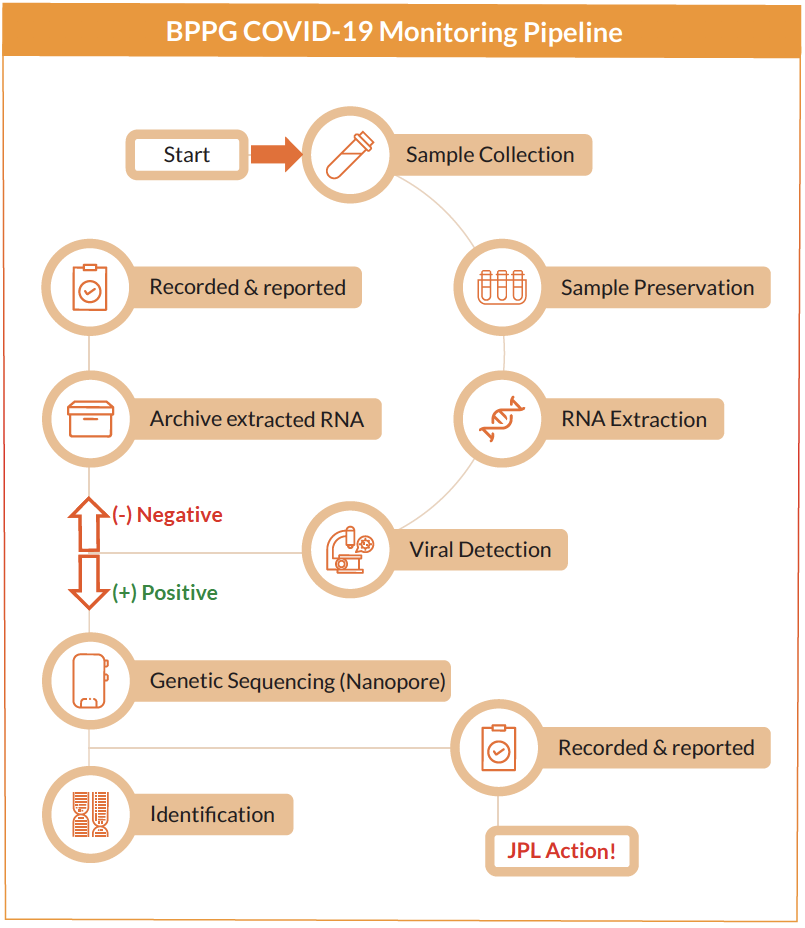
Simultaneously with COVID-19 monitoring, the JPL PP team developed strategies to protect JPLers through countermeasure cleaning methods. The methods included simple cleaning strategies, 80% alcohol with 20% Tween 20 (a detergent), as well as Kleenol, which is used to clean JPL’s Spacecraft Assembly Facility. After developing cleaning and countermeasure strategies, the PP team additionally proposed Research and Technology Development (R&TD) for developing novel defenses against COVID-19 and other microbes.
Key Elements
- JPL BBPG has expertise/facilities and outside partnerships for rapid COVID-19 detection.
- JPL PP team proposes a plan to environmentally monitor common areas such as conference rooms and clean rooms for COVID-19 by using CDC/NIH approved rapid qPCR assay.
- All negative samples will be archived and recorded.
- Presumptive positive samples will be confirmed through genetic sequencing, recorded, and reported to JPL management for additional action (i.e. cleaning, room isolation, recommendations for clinical testing for engineers).
- JPL PP team also developing cleaning and countermeasure strategies to mitigate COVID-19 virus.
Final conclusions from the COVID-19 environmental monitoring program noted that no positive SARS-CoV-2 samples were found on surfaces at JPL, but nevertheless new safety regulations were applied to all personnel who work at JPL. Until COVID-19 is contained worldwide, all JPL activities will adhere to commonly accepted public practices of physical distancing, cleaning workspaces at task start and at task end, separation of personnel into different working shifts, wearing face masks while on Lab, using hand sanitizer at building and bathroom entrances, and providing safety glasses for employees without eyeglasses. Finally, groups will explore options to increase safety while working on Lab. For example, PP engineers will separate shifts by at least a 1-hour margin to account for experiment delays and cleaning.
JPL and NASA have adapted to the new reality of living and working and in the midst of a pandemic. It is through our JPL spirit and tenacity that the BPPG team and will continue to support the success of NASA missions alongside JPL engineers, program managers, and the larger JPL family.
written by Zach Dean & Daniel Yoon
contributed by Camilla Urbaniak, Kasthuri Venkateswaran & Nitin Singh
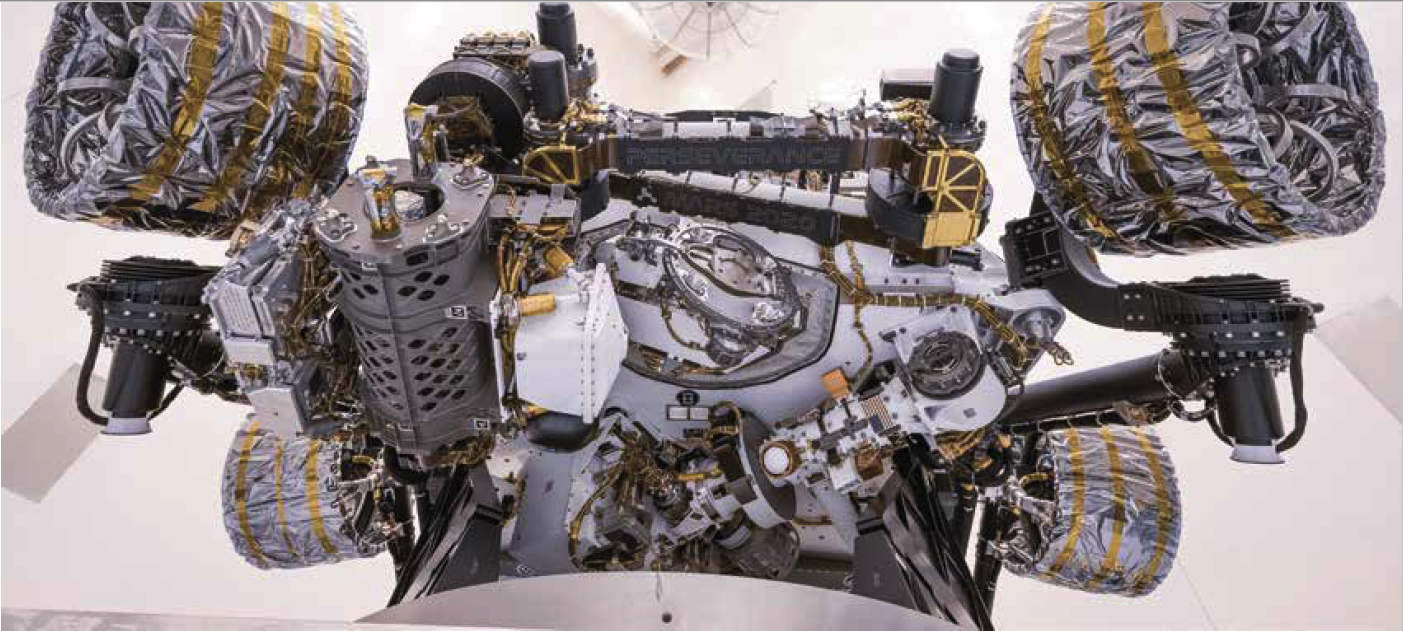
BPPG Mars 2020
PP Takes On Perseverance and Ingenuity
The Mars 2020 mission’s Perseverance Rover and Ingenuity Helicopter represent yet another major milestone for NASA's Mars Exploration Program, a long-term program for robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The Mars 2020 mission addresses high-priority science goals for Mars exploration, including key astrobiology questions about the potential for life on Mars. The mission's primary science objective is to not only seek signs of habitable conditions on Mars but also to search for signs of past microbial life as well.
In preparation for last year’s July 30th launch, more than a dozen PP team members supported the Assembly, Test and Launch Operations (ATLO) activities across the country, from Florida’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC) to Pasadena, California. To ensure that the spacecraft met the NASA biological cleanliness requirements, regular monitoring and sampling were critical for nearly two and a half years prior to ATLO. The final campaign culminated in a grand total of 16,881 samples collected including 9,664 spacecraft samples, 5,847 assembly and test facility samples, 1,052 ground support equipment samples, and 318 air samples.
While completing tasks at KSC, team members additionally adhered to strict guidelines to protect against COVID-19 exposure, a challenge unique to Mars 2020 compared to previous JPL flagship missions.
In addition to the flight implementation activities, the PP genetic inventory and archiving teams provided insightful data to the project. The requirements for both archiving and genetic inventory involve identifying, quantifying, and documenting potential pre-launch terrestrial contamination sources from both organic compounds and organisms. In addition, archiving and genetic inventory are tasked with providing mechanisms to support the characterization of round-trip terrestrial contamination. To accomplish these tasks, the teams identified microorganisms on Mars 2020 spacecraft using a mass spectrometer and DNA sequencer to help understand and control contamination sources, resulting in the discovery of a diverse and unique set of microorganisms, both spore-forming and non-spore-forming, on spacecraft surfaces and cleanrooms. Overall, these projects determined the “passenger list” for biological material inbound to Mars.
Planetary Protection efforts with Mars 2020 also resulted in the formation of new products and tools, which will provide in more efficient bioburden evaluation and tracking in future outer planets missions. In cooperation with NASA JPL’s Contamination Control Group, a Planetary Protection/Contamination Control Matrix was assembled to visualize the overlap between biological and chemical removal from spacecraft, saving time and minimizing confusion. A Heat Microbial Reduction Tracking Tool was assembled to automatically calculate and follow bioburden reduction. Planetary Protection Cert Logs were implemented to fully digitize certification for hardware owners and increase communication between teams. Finally, a Sampling Quantity and Alert Level Calculator was developed for determining the most efficient number of swabs and wipes needed in spacecraft (and facility) bio-sampling activities. With the July 2020 launch of Mars 2020, the accomplishment of all Planetary Protection team members is even more impressive given the ongoing challenges from COVID-19. Even a pandemic can’t stop space exploration and innovation!
written by Zach Dean & Emily Seto
contributed by Moogega Cooper & Daniel Yoon
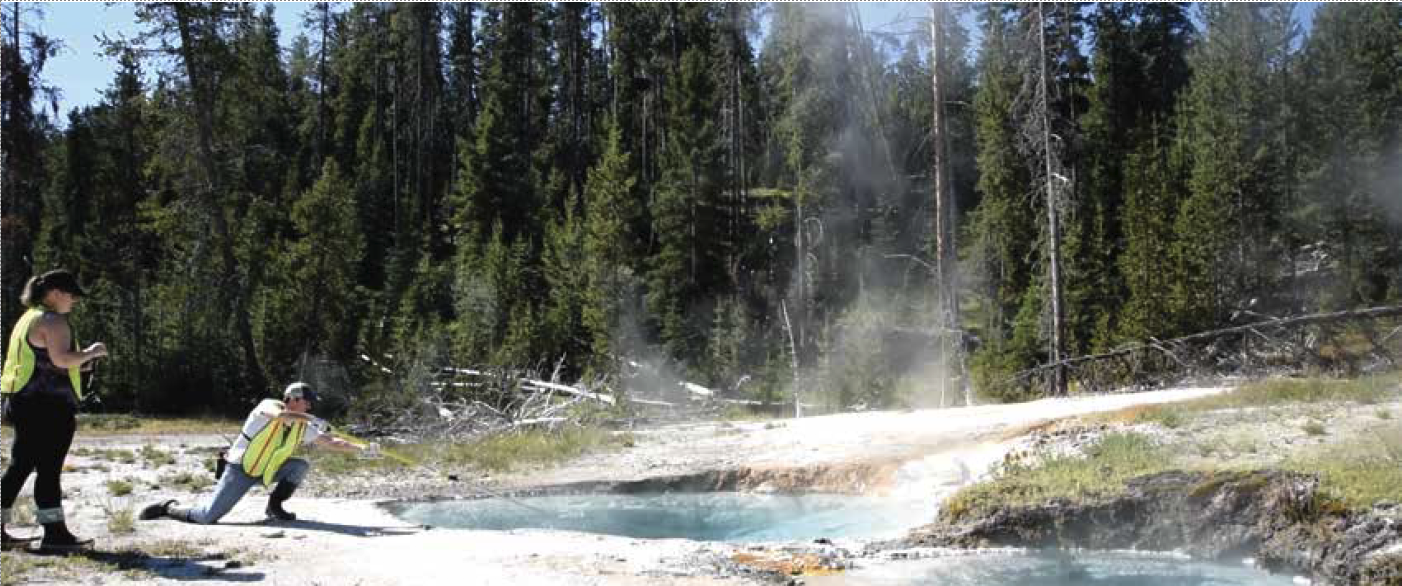
Yellowstone Microbes
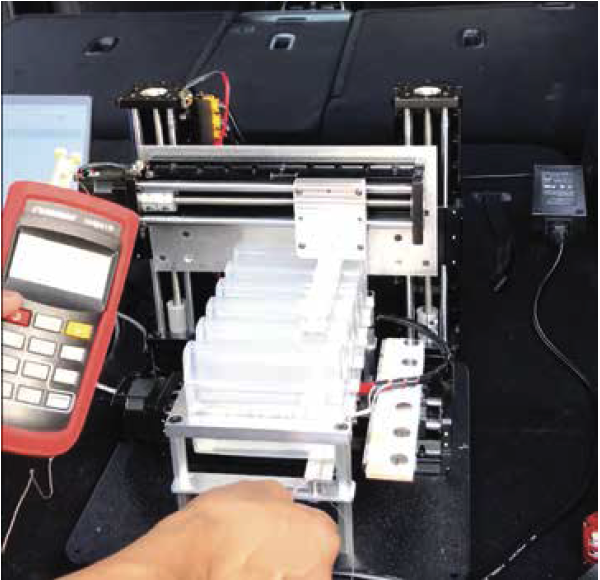
Our New Space Science Device, μTITAN
"“The Hot Springs at Yellowstone National Park provides an ideal environmental for studying microbial ecology because the hot springs have high and extreme biomass.”"
NASA has made great strides over the past five years in developing a suite of space-capable molecular biology instruments for the International Space Station. Despite the progress, however, a key piece of equipment that has been missing is a nucleic acid extraction instrument that can discern from an array of complex human and environmental samples. The Planetary Protection “Omics in Space” team has developed the ‘μTitan’, a micro gravity-tested instrument for automated nucleic acid extraction. The μTitan instrument is a compact, portable, robust, energy-efficient device that allows for streamlined and consistent nucleic acid extractions with minimal human labor.
The μTitan provides the ability to perform complex sample processing on the ISS to gather real-time information from DNA isolation, and it has been validated previously for successful extraction of RNA. The μTitan can therefore be used to process samples for microbiome, metagenome, transcriptome, and virome analyses on the ISS and possibility on other deep space missions. Additionally, the characteristics that make the μTitan advantageous for space travel also make it suitable for remote settings here on Earth.
The μTitan system was validated using a whole cell microbial reference (WCMR) standard comprised of nine bacteria titrated at concentrations designed to challenge the performance of the instrument as well as to resolve its detection limits for isolating DNA. Quantitative assessment of system performance was measured by comparing μTitan input challenge dose versus recovery by Qubit spectrofluorometry, RTqPCR, Bioanalyzer, and next-generation sequencing.
Overall, results indicate that the μTitan system performs equal to or better than similar commercially available, Earth-based, automated nucleic acid extraction devices. The μTitan system was also tested in Yellowstone National Park with the WCMR to mimic use in a remote setting with limited resources. The performance of the device at Yellowstone was also comparable to use in a laboratory setting. In fact, the μTitan system even supplied improvements over typical laboratory devices, providing results in almost real time as opposed to days or weeks later. Such a portable, field-deployable, nucleic extraction system will be valuable for environmental microbiology, as well as for health care diagnostics in preventing microbial diseases.
Whether the μTitan system is used on the ISS or on Earth, it provides high-quality nucleic acid material for functional genomics, microbial monitoring, and detection of biological signatures related to human health and engineering systems. With this technology, JPL will be able to analyze microbial dynamics in-space stations as well as tomorrow’s space-science to the moon, on Mars, and beyond.
written by Daniel Yoon
contributed by Kasthuri Venkateswaran
Other Stories
HBCUs Team Up With PPCoE for 2020 Summer Bioinformatics Workshop
In addition to the hundreds of interns participating virtual internships across JPL last summer, the PP CoE’s HBCU workshop was also bit different from the previous in-person sessions due to COVID-19. The program was virtual and was designed to introduce computer science students from Howard University and Tuskegee University to bioinformatics, and show how their specific coding skills could be useful for solving real world NASA problems. Additionally, we wanted these students to grasp the concept of collaborating on a project virtually and working with cloud instances.
Eventhough it was a truncated 5-week program the students were very sincere and showed genuine interest in the field. They were all quick learners and eager to do the work. Dr. Chiranjit Mukherjee, one of the program instructors, expressed just how impressive these students were, saying, “I have worked with undergraduates both in the setting of formal classroom teaching and as a research mentor, and these students were some of the best I have worked with.” JPL and the PP CoE are excited to imlplement future programs with these universities in 2021.
written by Alvin Smith
contributed by Mukherjee, Chiranjit
Planetary Protection Article Tops the Charts!!
According to Almetric, a system that tracks the attention that research outputs such as scholarly articles and datasets receive online, the PP article entitled “Characterization of the total and viable bacterial and fungal communities associated with the International Space Station surfaces” received the most online attention related to microbiome research in 2020.
This article, co-authored by several BPPG postdocs including Principal Investigator, Dr. Kasthuri Venkateswaran, described the diversity of microbes that survive in the ISS, and used molecular and culture-based methods to assess microbial communities on ISS surfaces.
This article scored in the 99th percentile of the 269,976 tracked articles of a similar age in all journals and the top percentile (ranked 1st) of the tracked articles of a similar publication date in Microbiome. A key difference between Altmetric and other social media monitoring services is that Altmetric will disambiguate links to outputs: it knows that even though some tweets might link to a PubMed abstract, newspapers to the publisher's site and blog posts to a dx.doi.org link they're all talking about the same paper.
written by Daniel Yoon
contributed by Kasthuri Venkateswaran
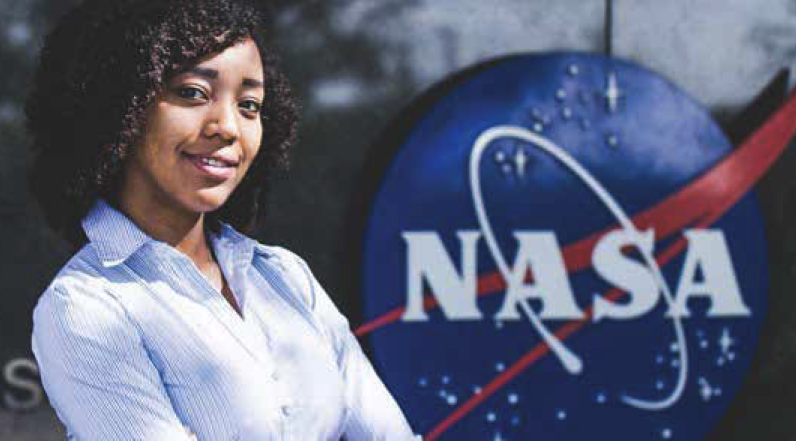
PP Spotlight: Dr. Moogega Cooper
Dr. Moogega “Moo” Cooper, was selected to co-host the NASA Live stream launch of the Mars 2020 rover, on July 30, 2020. Moo is a scientist in the Biotechnology Planetary Protection Group at JPL, and the Planetary Protection Lead for the Mars 2020 Mission. During the Mars 2020 rover flight preparation, her main task was to coordinate the PP lab team at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) and manage the team in completing PP flight implementation through Assembly Test and Launch Operations.
While at KSC, she was contacted by NASA leadership with a unique opportunity to potentially co-host the launch at Cape Canaveral. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, KSC was already limiting the number of people at the center, so this opportunity was not confirmed unitl launch day.
When asked what this co-hosting opportunity meant to her, Dr. Cooper said, “I had the duty to translate the play-by-play that lead to launch day in a fun and meaningful way to the world. As a black woman, I also felt it was important to represent a face that I hope future generations will find commonplace when thinking about people who are involved with building spacecraft. It starts with a spark and I hope to do my part in showing kids that they can grow and thrive in the field of space exploration.” Well done PP team. Go Perseverance!
written by Daniel Yoon
contributed by Moogega Cooper
Important Dates
April 17, 2021
Connect With Us
Planetary Protection Center of Excellence
Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Editor: Daniel Yoon and Alvin Smith
Email us at: planetprotection.coe@jpl.nasa.gov